Fourier
Definition
Assembly: Meta.Numerics (in Meta.Numerics.dll) Version: 4.2.0+6d77d64445f7d5d91b12e331399c4362ecb25333
public sealed class FourierTransformerPublic NotInheritable Class FourierTransformerpublic ref class FourierTransformer sealed[<SealedAttribute>]
type FourierTransformer = class end- Inheritance
- Object FourierTransformer
Remarks
A Fourier transform decomposes a function into a sum of different frequency components. This is useful for a wide array of applications.
Mathematically, the DFT is an N-dimensional linear transfromation with coefficients that are the Nth complex roots of unity.
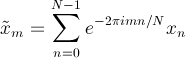
An instance of the FourierTransformer class performs DFTs on series of a particular length, given by its Length property. This specialization allows certain parts of the DFT calculation, which are indepdent of the transformed series but dependent on the length of the series, to be performed only once and then re-used for all transforms of that length. This saves time and improves performance. If you need to perform DFTs on series with different lengths, simply create a seperate instance of the FourierTransform class for each required length.
Many simple DFT implementations require that the series length be a power of two (2, 4, 8, 16, etc.). Meta.Numerics supports DFTs of any length. Our DFT implementation is fast -- order O(N log N) -- for all lengths, including lengths that have large prime factors.
Example
The following code performs a simple DFT and then inverts it to re-obtain the original data.
// Create a Fourier transformer for length-6 series
FourierTransformer ft = new FourierTransformer(6);
// Create a length-6 series and transform it
Complex[] x = new Complex[] { 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0 };
Complex[] xt = ft.Transform(x);
// Re-use the same transformer to transform a different series
Complex[] y = new Complex[] { 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 };
Complex[] yt = ft.Transform(y);
// Transform them back
Complex[] xtt = ft.InverseTransform(xt);
Complex[] ytt = ft.InverseTransform(yt);Constructors
| FourierTransformer(Int32) | Initializes a new instance of the Fourier transformer. |
| FourierTransformer(Int32, FourierSign, FourierNormalization) | Initializes a new instance of the Fourier transformer with the given sign and normalization conventions. |
Properties
| Length | The series length for which the transformer is specialized. |
| NormalizationConvention | Gets the normalization convention used by the transformer. |
| SignConvention | Gets the normalization convention used by the transformer. |
Methods
| Equals | Determines whether the specified object is equal to the current object. (Inherited from Object) |
| GetHashCode | Serves as the default hash function. (Inherited from Object) |
| GetType | Gets the Type of the current instance. (Inherited from Object) |
| InverseTransform | Computes the inverse Fourier transform of the given series. |
| ToString | Returns a string that represents the current object. (Inherited from Object) |
| Transform | Computes the Fourier transform of the given series. |