Meta.Numerics Library
Weibull
Represents a Weibull distribution.
Definition
Namespace: Meta.Numerics.Statistics.Distributions
Assembly: Meta.Numerics (in Meta.Numerics.dll) Version: 4.2.0+6d77d64445f7d5d91b12e331399c4362ecb25333
Assembly: Meta.Numerics (in Meta.Numerics.dll) Version: 4.2.0+6d77d64445f7d5d91b12e331399c4362ecb25333
C#
public sealed class WeibullDistribution : ContinuousDistributionVB
Public NotInheritable Class WeibullDistribution
Inherits ContinuousDistributionC++
public ref class WeibullDistribution sealed : public ContinuousDistributionF#
[<SealedAttribute>]
type WeibullDistribution =
class
inherit ContinuousDistribution
end- Inheritance
- Object UnivariateDistribution ContinuousDistribution WeibullDistribution
Remarks
The Weibull distribution is a generalized form of the exponential distribution, for which the hazard function is not constant, but instead increases (for shape parameter k > 1) or decreases (for shape parameter k < 1) with x. When the shape parameter is one, the Weibull distribution reduces to the exponential distribution.
In fact, any Weibull distribution can be transformed into a standard exponential distribtuion by a change of variables.
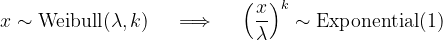
The Weibull distribution is commonly used in engineering applications to model the time-to-failure of industrial components.
Constructors
| WeibullDistribution | Initializes a new Weibull distribution. |
Properties
| ExcessKurtosis |
Gets the excess kurtosis of the distribution.
(Inherited from UnivariateDistribution) |
| Mean |
Gets the mean of the distribution.
(Overrides UnivariateDistributionMean) |
| Median |
Gets the median of the distribution.
(Overrides ContinuousDistributionMedian) |
| Scale | Gets the scale parameter of the distribution. |
| Shape | Gets the shape parameter of the distribution. |
| Skewness |
Gets the skewness of the distribution.
(Inherited from UnivariateDistribution) |
| StandardDeviation |
Gets the standard deviation of the distribution.
(Inherited from UnivariateDistribution) |
| Support |
Gets the interval over which the distribution is non-vanishing.
(Overrides ContinuousDistributionSupport) |
| Variance |
Gets the variance of the distribution.
(Overrides UnivariateDistributionVariance) |
Methods
| CentralMoment |
Computes a central moment of the distribution.
(Overrides ContinuousDistributionCentralMoment(Int32)) |
| Cumulant |
Computes a cumulant of the distribution.
(Inherited from UnivariateDistribution) |
| Equals | Determines whether the specified object is equal to the current object. (Inherited from Object) |
| ExpectationValue |
Computes the expectation value of the given function.
(Inherited from ContinuousDistribution) |
| FitToSample | Computes the Weibull distribution that best fits the given sample. |
| GetHashCode | Serves as the default hash function. (Inherited from Object) |
| GetRandomValue |
Generates a random variate.
(Overrides ContinuousDistributionGetRandomValue(Random)) |
| GetRandomValues |
Generates the given number of random variates.
(Inherited from ContinuousDistribution) |
| GetType | Gets the Type of the current instance. (Inherited from Object) |
| Hazard |
Computes the hazard function.
(Overrides ContinuousDistributionHazard(Double)) |
| InverseLeftProbability |
Returns the point at which the cumulative distribution function attains a given value.
(Overrides ContinuousDistributionInverseLeftProbability(Double)) |
| InverseRightProbability |
Returns the point at which the right probability function attains the given value.
(Overrides ContinuousDistributionInverseRightProbability(Double)) |
| LeftProbability |
Returns the cumulative probability to the left of (below) the given point.
(Overrides ContinuousDistributionLeftProbability(Double)) |
| ProbabilityDensity |
Returns the probability density at the given point.
(Overrides ContinuousDistributionProbabilityDensity(Double)) |
| RawMoment |
Computes a raw moment of the distribution.
(Overrides ContinuousDistributionRawMoment(Int32)) |
| RightProbability |
Returns the cumulative probability to the right of (above) the given point.
(Overrides ContinuousDistributionRightProbability(Double)) |
| ToString | Returns a string that represents the current object. (Inherited from Object) |